What is a DAC?
Given the complexity, scale, and diversity of global submitters and studies, the EGA operates a distributed data access model in which requests are made to the data controller, not to the EGA.
The European Commission defines a data controller, in the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), as the person that determines the purposes for which and the means by which personal data is processed.
A Data Access Committees, commonly referred to as DACs, comprise on or more individuals (or data controllers) that review data access requests and make decisions on who can access personally identifiable genetic, phenotypic, and clinical data deposited at the EGA. Therefore, the members of a DAC should be individuals who have the authority to approve data access requests.
The animation describes how you can authorise access to your sensitive data with the help of Data Access Committee and Authorisation tool. Acknowledgement to CSC - IT Center for Finland, Elixir Finland, Elixir Europe.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I create a Data Access Committee?
How can I create a Data Access Committee?
The members of a DAC can come from different areas of expertise, such as data management, data analysis, information technology, legal and compliance, subject matter experts, privacy and security, and representatives from the organisations or individuals that provide data to the DAC.
The specific members of a DAC can vary depending on the needs of the organisation and the type of data being managed. The EGA strongly suggests checking with your organisation to align with its regulations
How should a DAC be named?
The chosen name must be informative to the applicant. For example, internal identifiers, such as grant numbers, should not be used. Individual PI names should also not be used. DAC's are often named after the organisation or department of the data source.
How can I become an EGA DAC contact?
To register a DAC at the EGA you must create first as an EGA user. Once your EGA user has been approved by the Helpdesk team, you will be able to log in to the DAC Portal.
How can I register a DAC?
To register a DAC, follow the DAC Portal instructions. You will be required to provide a DAC name, name of the individual(s) that make up your DAC and contact details for your DAC including your Institutional email(s). Wherever possible, the DAC should make sure that all points of contact are readily available and able to answer any initial data requests/queries in < 2 weeks.
Once your DAC is registered, you will have to wait upon the validation from our Helpdesk team. As soon as all the validations have been completed, your DAC will be activated.
Alternatively, you can also establish a DAC at the EGA during a programmatic submission through Webin API.
Which are the possible roles of a DAC contact?
There are two possible roles for DAC contacts: member and admin. An admin has additional privileges compared to a member:
- An “admin” can manage data requests, create and edit policies, edit the content of the DAC, add or remove contacts, and decide the role of each contact.
- A “member” can manage data requests and create policies. However, a member does not have permission to modify DAC details, edit information from policies where they are not admins, or add/remove contacts.
There is no limit to the number of admins in a DAC, and each admin is responsible for deciding who should have editing privileges. This allows for a more decentralised and democratic approach to managing the DAC.
How can I modify the information of a DAC?
To modify a DAC, follow the instructions here. Keep in mind that only DAC contact with an admin role can modify the information of a DAC.
If your DAC was registered before the lauch of the DAC Portal, and its ID is EGAC0 (not EGAC5), you must use the programmatic submission to modify it. Please, do not hesitate to contact our Helpdesk team if you need help with this!
To prevent potential data breaches and ensure adherence to GDPR regulations, it is essential that the European Genome-Phenome Archive (EGA) is informed via the Helpdesk team of any changes to the Data Access Committee (DAC). This should be done in addition to any changes being made on the DAC portal. Data Controllers (as per the definition in the DPA) are also responsible for notifying the previous DAC of any modifications. Without proper notification, changes might not be automatically updated in our system, leading to the risk of incorrect permissions being applied and potential data access issues. Therefore, it is imperative that all Data Controllers follow this protocol to maintain data integrity and security.
What’s the link between DAC, policy and dataset?
A dataset is linked to one single policy. At the same time, one policy has a one to one relationship with a DAC.

In this example, you can see that in this dataset page, we are only showing the information of one DAC (1 dataset - 1 DAC).
However, the ratio of objects does not work the same in the other direction. One DAC can own multiple policy objects. And each policy object can be reused in several datasets. Thus, one DAC can manage one or more datasets.
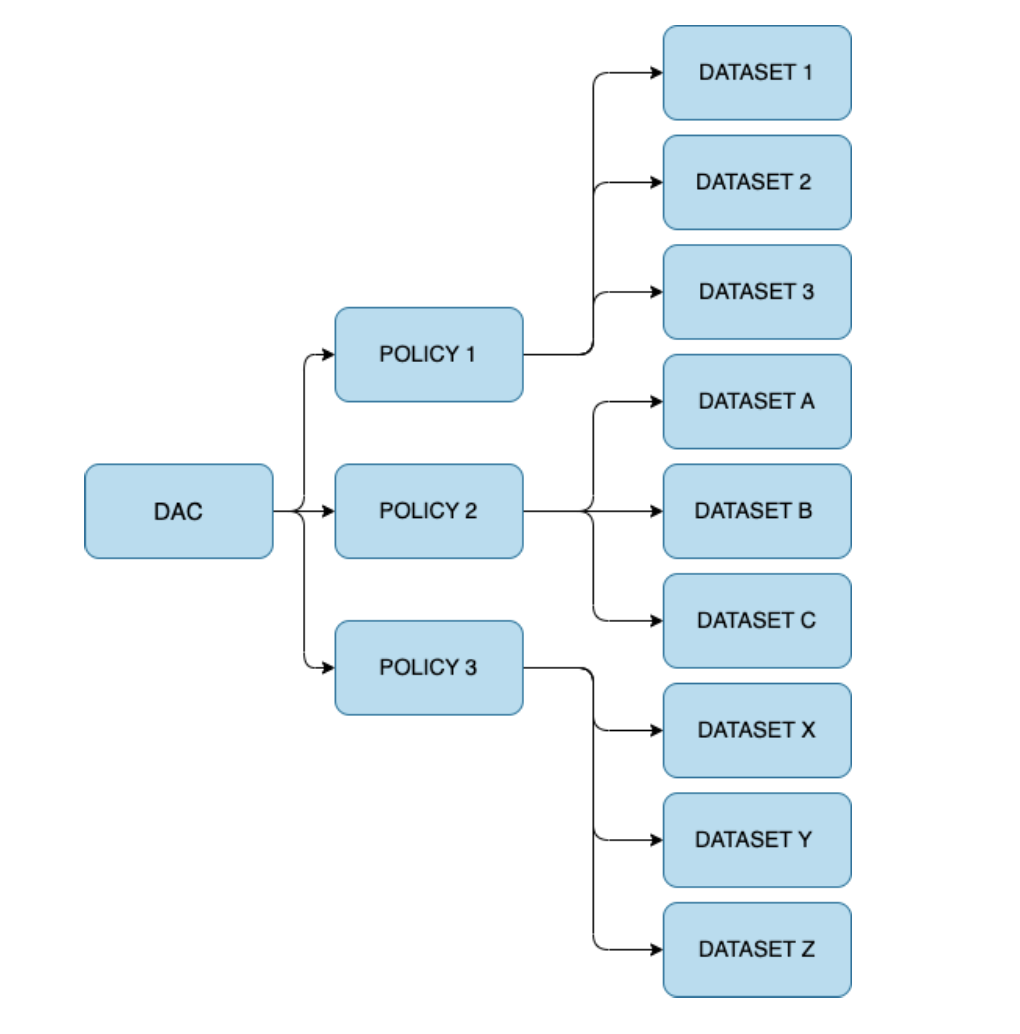
In this example, you can see that in this DAC page, we are showing all the datasets that are managed by one DAC (1 DAC - >400 datasets).
EGA Data Access Committee Best Practices
Which are the EGA DAC best practices?
Refer to DAC Best Practices
What happens if a DAC member changes institutions?
EGA is committed to the protection and ownership of the data stored in our systems. We respect the institution's ownership of the data, and as such, if a DAC member changes institutions, the ownership of the data will not be transferred to the new institution.
Therefore, before changing institutions, we request that the DAC contact add a new member who will replace them once they no longer work at the institution. This ensures that the data remains protected and is accessible to authorised personnel at the institution.
To prevent potential data breaches and ensure adherence to GDPR regulations, it is essential that the European Genome-Phenome Archive (EGA) is informed via the Helpdesk team of any changes to the Data Access Committee (DAC). This should be done in addition to any changes being made on the DAC portal. Data Controllers (as per the definition in the DPA) are also responsible for notifying the previous DAC of any modifications. Without proper notification, changes might not be automatically updated in our system, leading to the risk of incorrect permissions being applied and potential data access issues. Therefore, it is imperative that all Data Controllers follow this protocol to maintain data integrity and security.
What happens if EGA detects an unresponsive DAC?
EGA defines an unresponsive DAC as a DAC with one or more contacts who do not respond to data access requests. EGA has procedures in place to identify these types of DACs, escalate the issue, and attempt to reassign the DAC to a responsive contact. This is a crucial step in ensuring that data can be accessed and utilised by researchers.
If EGA identifies an unresponsive DAC, the organisation will first try to resolve the issue by escalating it to the appropriate parties. This may involve attempting to reassign the DAC to a more responsive contact.
Unfortunately, in situations where we cannot reassign the DAC, the dataset will be withdrawn from the public website and the files will be removed from our system. If an EGA ID is referenced in a publication, the EGA will take extra steps to ensure that the public is made aware of the data's unavailability.
I don't want to receive an email notification for pending requests. How can I do that?
If you are an EGA DAC with pending requests, you will always receive emails for new data access requests.
However, the EGA understands that a request resolution can take some time, for this reason, if you add a comment (make sure you save it by clicking the APPLY button!) we will filter those requests at the time of sending the notification!
How can I manage data access requests?
What documentation does the DAC need to provide?
Each dataset that is submitted to the EGA must be linked to a policy object. The policy is a Data Access Agreement (DAA), which defines the terms and conditions of using the dataset, such as how the data files should be stored once downloaded or details of publication embargoes that should be observed by the approved user.
As part of the Data Access Agreement, information regarding the application can be captured to help inform the DAC when making its decision. For example, requestors could be asked to provide a proposed title for their research and a proposal of how the data will be used. By asking for provision of such information the DAC can be assured that the requestor fully understands any consents associated with the data. It is important that accounts created at the EGA, are created solely for those individuals that will be downloading the data from the EGA. As part of the data access request, we strongly encourage you to identify individuals that will need an account at the EGA in order to prevent sharing of login details, which is strictly prohibited under EGA user account policy. Such information can easily be captured in the DAA.
NOTICE The data access agreement template below is provided for guidance only and should be adapted as you see fit to suit your own purpose. In the interest of promoting data sharing, we suggest that if an agreement cannot be met around clause 19 in this example that both parties should agree to remain silent, and that the clause should be removed from the agreement.
Example DAAHow can the DAC provide the DAA?
The DAC should provide their own DAA when registering a policy. Data requestors will download this document and should fill it in and send it back to the DAC. Data access decisions should be based on such documentation.
The DAA can be downloaded through the request data webpage. Once it has been filled in, the signed copy of the DAA can be uploaded back to the request data webpage and sent to the DAC for review.
How can I grant access to the data?
Once you receive a data access request, you can login to the DAC Portal. In this portal you will see all your pending requests and will be able to grant or decline access to the requestors.
I am a member of the Data Access Committee. Could I approve somebody else to deal with the requests on my behalf?
If you want to delegate data access decisions to someone else, make sure that the individual's account is officially registered as a member of the DAC.
Remember that a DAC contact with an "admin" role can always add new members to an existing DAC, remove members, and modify contact details through the DAC Portal.
Can I automatise the process of managing data access requests?
The answer is yes! You can use a programmatic approach using our DAC API!
Check out the DAC API specification!Data Breach
What should a DAC do if they suspect a breach?
If a DAC suspects a data breach of one or more of their datasets, they should immediately contact the EGA Helpdesk team at this link. The DAC must provide the following information when contacting the EGA Helpdesk team:
- A list of affected datasets
- An estimated date of the data breach (or interval of dates)
- A list of unauthorised users who accessed the data (if available). Otherwise, they can provide a list of authorised users for the affected datasets
- Any observations they would like to raise to the EGA team
Once the DAC has contacted the EGA team, we will respond within 48 hours (please allow some leeway during peak times) and activate our data breach protocol.
What can I expect from the EGA if they detect a breach?
Once the EGA determines that a security incident has occurred, we will notify all DAC members that a data breach has been detected, and take steps to contain the incident. Containment approaches may include:
- Revoking a data provider's access to the EGA resources, such as by changing passwords.
- Removing affected EGA datasets from distribution, such as by withdrawing a dataset.
- Disabling certain functions or services, such as the EGA ingestion pipeline.
- Shutting down the system or disconnecting it from the network.
After the incident has been contained, the EGA will determine whether it is necessary to eradicate components related to the incident. Finally, the EGA will enable recovery of the service to normal operation and confirm that all services are functioning normally.
